For each enabled interface, you can see detailed information such as OSPF area ID, OSPF process ID, network type, and how the interface was included into the OSPF process.
The show ip ospf neighbor command displays OSPF neighbor information on a per-interface basis. The significant fields of the output include Neighbor ID, Priority, State, Dead Time, Address, and Interface. This command does not provide the network type being used by OSPF.
The show ip protocols command is used to show the parameters and the current state of the active routing protocol process. For OSPF, it will display information such as the OSPF router ID, number of areas in this router, and the area type. This command does not provide the network type being used by OSPF.
The show ip route ospf command gives you clearly separated lists of intra-area and inter-area routes. In addition, the output of the command gives you essential information about area border routers. This includes the router ID, IP address in the current area, the interface that advertises routes into the area, and the area ID. This command does not provide the network type being used by OSPF.
You want to choose a fast, scalable non-proprietary routing protocol for your network, what is the best choice?
B. OSPF
The default-information originate command is used to generate a default
external route from EIGRP into an OSPF routing domain. It is not used to configure
an EIGRP default route.
Correct. OSPFv2 uses a built-in authentication mechanism and supports plaintext and hashing with MD5 or SHA.
Incorrect. Encryption is not supported in OSPFv2. However, IPsec can be used with OSPFv3.
Correct. Simple passwords are supported but not recommended.
Incorrect. SHA is supported by OSPFv2, but the standard specie SHA-2.
Question: Refer to the exhibit. You want to ensure that traffic from R1 to Network A uses the AS path through ABR2.
Which three configurations would accomplish this task?
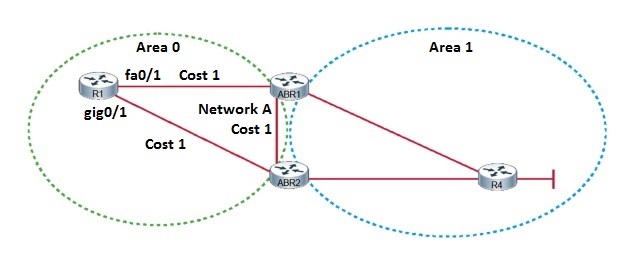
Correct answer: B C D
Your answer: B D F
Explanation: With OSPF, the paths with the lowest costs are selected as the best paths. In this case, both paths have the same cost, so the router will perform equal-cost load balancing. To ensure that traffic from R1 to Network A uses the AS path through ABR2, you need to ensure that it has the lowest cost. Cost is calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the interface bandwidth. The cost value is a 16-bit positive number between 1 and 65,535, and the reference bandwidth is set to 100 Mbps by default. Since Fast Ethernet and higher links have an interface bandwidth of 100 Mbps or higher, they are all assigned a cost of 1. By adjusting the reference bandwidth to a higher value using the auto-cost reference-bandwidth OSPF configuration command, the cost of the Fast Ethernet link will be higher than the Gigabit Ethernet link. The reference bandwidth value is inserted in Mbps, so a value of 1000 would assign a cost of 10 to the Fast Ethernet link, and a cost of 1 would be assigned to the Gigabit Ethernet link.
With OSPF, the paths with the lowest costs are selected as the best paths. In this case, both paths have the same cost, so the router will perform equal-cost load balancing. To ensure that traffic from R1 to Network A uses the AS path through ABR2, you need to ensure that it has the lowest cost. Cost is calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the interface bandwidth. The cost value is a 16-bit positive number between 1 and 65,535, and the reference bandwidth is set to 100 Mbps by default. By manually adjusting the cost for a link, you can influence the OSPF path preference. To adjust the cost of a link, you need to use the ip ospf cost interface command. In this case, adjusting the cost of the Fast Ethernet link to 10, will ensure that the Gigabit Ethernet link will be used to route traffic to Network A as it has a cost of 1.
With OSPF, the paths with the lowest costs are selected as the best paths. In this case, both paths have the same cost, so the router will perform equal-cost load balancing. To ensure that traffic from R1 to Network A uses the AS path through ABR2, you need to ensure that it has the lowest cost. Cost is calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the interface bandwidth. By adjusting the bandwidth of a specific interface, you can influence OSPF path preference for a specific link. To do this, you need to use the bandwidth command in interface configuration mode, which expresses a bandwidth in Kbps. In this case, adjusting the bandwidth of the Fast Ethernet link to 10,000 Kbps (10 Mbps), you change the cost of this link to 10. Since the Gigabit Ethernet link now has a lower cost, it will be used to route traffic to Network A.
Link cost is calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the interface bandwidth. The cost value is a 16-bit positive number between 1 and 65,535, and the reference bandwidth is set to 100 Mbps by default. Changing the reference bandwidth to 10 will not change the costs of Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet links. Both links have interface bandwidths over 10 Mbps, so they still will have costs of 1. In this case, both paths have the same cost, so the router will perform equal-cost load balancing.
With OSPF, the paths with the lowest costs are selected as the best paths. By changing the cost of the Gigabit Ethernet link to 10 Mbps, OSPF will use the Fast Ethernet link to ABR1 as it has a cost of 1.
Link cost is calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the interface bandwidth. The cost value is a 16-bit positive number between 1 and 65,535, and the reference bandwidth is set to 100 Mbps by default. By setting the interface bandwidth of the Gigabit Ethernet interface to 100,000 Kbps (100 Mbps), the cost of the link will remain at 1. In this case, both paths have the same cost, so the router will perform equal-cost load balancing.
You can use the "ip ospf message-digest-key" command is used to assign a key ID and key to use with neighboring OSPF MD5 routers.
You must specify if MD5 or a plaintext password is to be used.
You must use the message-digest option.
You can use ip ospf message-digest-key command to configure MD5 authentication.
Correct. OSPFv2 uses a built-in authentication mechanism and supports plaintext and hashing with MD5 or SHA.
Incorrect. Encryption is not supported in OSPFv2. However, IPsec can be used with OSPFv3.
Correct. Simple passwords are supported but not recommended.
Incorrect. SHA is supported by OSPFv2, but the standard specie SHA-2.
Question: Refer to the exhibit. You want to ensure that traffic from R1 to Network A uses the AS path through ABR2.
Which three configurations would accomplish this task?

A. R1(config)# interface gig0/1
R1(config-if)# ip ospf cost 10
R1(config-if)# ip ospf cost 10
B. R1(config)# interface fa0/0
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 10000
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 10000
C. R1(config)# router ospf 1
R1(config-router)# auto-cost reference-bandwidth 1000
R1(config-router)# auto-cost reference-bandwidth 1000
D. R1(config)# interface fa0/0
R1(config-if)# ip ospf cost 10
R1(config-if)# ip ospf cost 10
E. R1(config)# router ospf 1
R1(config-router)# auto-cost reference-bandwidth 10
R1(config-router)# auto-cost reference-bandwidth 10
F. R1(config)# interface gig0/1
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 100000
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 100000
Correct answer: B C D
Your answer: B D F
Explanation: With OSPF, the paths with the lowest costs are selected as the best paths. In this case, both paths have the same cost, so the router will perform equal-cost load balancing. To ensure that traffic from R1 to Network A uses the AS path through ABR2, you need to ensure that it has the lowest cost. Cost is calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the interface bandwidth. The cost value is a 16-bit positive number between 1 and 65,535, and the reference bandwidth is set to 100 Mbps by default. Since Fast Ethernet and higher links have an interface bandwidth of 100 Mbps or higher, they are all assigned a cost of 1. By adjusting the reference bandwidth to a higher value using the auto-cost reference-bandwidth OSPF configuration command, the cost of the Fast Ethernet link will be higher than the Gigabit Ethernet link. The reference bandwidth value is inserted in Mbps, so a value of 1000 would assign a cost of 10 to the Fast Ethernet link, and a cost of 1 would be assigned to the Gigabit Ethernet link.
With OSPF, the paths with the lowest costs are selected as the best paths. In this case, both paths have the same cost, so the router will perform equal-cost load balancing. To ensure that traffic from R1 to Network A uses the AS path through ABR2, you need to ensure that it has the lowest cost. Cost is calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the interface bandwidth. The cost value is a 16-bit positive number between 1 and 65,535, and the reference bandwidth is set to 100 Mbps by default. By manually adjusting the cost for a link, you can influence the OSPF path preference. To adjust the cost of a link, you need to use the ip ospf cost interface command. In this case, adjusting the cost of the Fast Ethernet link to 10, will ensure that the Gigabit Ethernet link will be used to route traffic to Network A as it has a cost of 1.
With OSPF, the paths with the lowest costs are selected as the best paths. In this case, both paths have the same cost, so the router will perform equal-cost load balancing. To ensure that traffic from R1 to Network A uses the AS path through ABR2, you need to ensure that it has the lowest cost. Cost is calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the interface bandwidth. By adjusting the bandwidth of a specific interface, you can influence OSPF path preference for a specific link. To do this, you need to use the bandwidth command in interface configuration mode, which expresses a bandwidth in Kbps. In this case, adjusting the bandwidth of the Fast Ethernet link to 10,000 Kbps (10 Mbps), you change the cost of this link to 10. Since the Gigabit Ethernet link now has a lower cost, it will be used to route traffic to Network A.
Link cost is calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the interface bandwidth. The cost value is a 16-bit positive number between 1 and 65,535, and the reference bandwidth is set to 100 Mbps by default. Changing the reference bandwidth to 10 will not change the costs of Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet links. Both links have interface bandwidths over 10 Mbps, so they still will have costs of 1. In this case, both paths have the same cost, so the router will perform equal-cost load balancing.
With OSPF, the paths with the lowest costs are selected as the best paths. By changing the cost of the Gigabit Ethernet link to 10 Mbps, OSPF will use the Fast Ethernet link to ABR1 as it has a cost of 1.
Link cost is calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the interface bandwidth. The cost value is a 16-bit positive number between 1 and 65,535, and the reference bandwidth is set to 100 Mbps by default. By setting the interface bandwidth of the Gigabit Ethernet interface to 100,000 Kbps (100 Mbps), the cost of the link will remain at 1. In this case, both paths have the same cost, so the router will perform equal-cost load balancing.
You can use the "ip ospf message-digest-key" command is used to assign a key ID and key to use with neighboring OSPF MD5 routers.
You must specify if MD5 or a plaintext password is to be used.
You must use the message-digest option.
You can use ip ospf message-digest-key command to configure MD5 authentication.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Thank you for your comment. Will try to react as soon as possible.
Regards,
Networ King